
I have analyzed a dataset involving all 84 chips and lasting for 62 minutes. The run suffered from poor seeing, with FWHM ranging from 5-8 arcseconds. No promising candidates were found.
The dataset "20191203" is based on images acquired during UT 2019 Dec 03. The images cover the span of time
2458821.10659 ≤ JD ≤ 2458821.14962
which is about 62 minutes.
The FITS headers of one of these images states, in part:
OBJECT = 'J0433+1939_dith1' / object name EXPTIME = 119.988480 / [s] total exposure time TELAPSE = 120.500020 / [s] elapsed time EXPTIME1= 0.999904 / [s] exposure time per frame TFRAME = 1.000000 / [s] frame interval in seconds DATA-FPS= 1.000000 / [Hz] frame per second DATA-TYP= 'OBJECT' / data type (OBJECT,FLAT,DARK) OBS-MOD = 'Imaging' / observation mode FILTER = 'BLANK' / filter name PROJECT = 'Earth Shadow Survey (1Hz)' / project name OBSERVER= 'Noriaki Arima' / observer name PIPELINE= 'wcs,stack,raw' / reduction pipeline templete
The images were reduced and cleaned by others; I started with clean versions of the images. Each set of 120 images was packed into a single FITS file, covering a span of (120 * 1.0 sec) = 120 seconds. These "chunk" files were located on shinohara in the directory
/gwkiso/tomoesn/raw/20191203
with names like
rTMQ1201912030019167511.fits
These names can be decoded as follows:
r stands for "reduced" ??
TMQ1 means "Tomoe data, part of quadrant 1"
20191203 means year 2019, month 12, day 03
00191675 means chunk index 00191675 (increases with time)
11 means chip 11
.fits means a FITS file
I'll refer to each of these "composite" files as a "chunk".
There are typically 30 chunks for each chip, and a total of 2492 chunks in the entire dataset. Each chunk file was 1083 MByte, so the total volume of the chunk files was about 2699 GByte = 2.7 TByte.
I ran a slightly modified version of the Tomoe pipeline on the images; it was not the same as that used to analyze the 2016 images discussed in the transient paper for two reasons:
The main stages in the pipeline were:
The output of the pipeline includes a copy of each FITS image, plus a set of ASCII text files which include both the raw, uncalibrated star lists, and the calibrated versions of those lists, as well as the ensemble output.
After running the pipeline to reduce the data, clean the images, find and measure stars, calibrate them astrometrically and photometrically, I used a script to look at properties of the data over the course of the night. You can read more about the "weather" in another note.
Below are links to the graphs produced for each of the 4 quadrants.
Quadrant 1:

Quadrant 2:
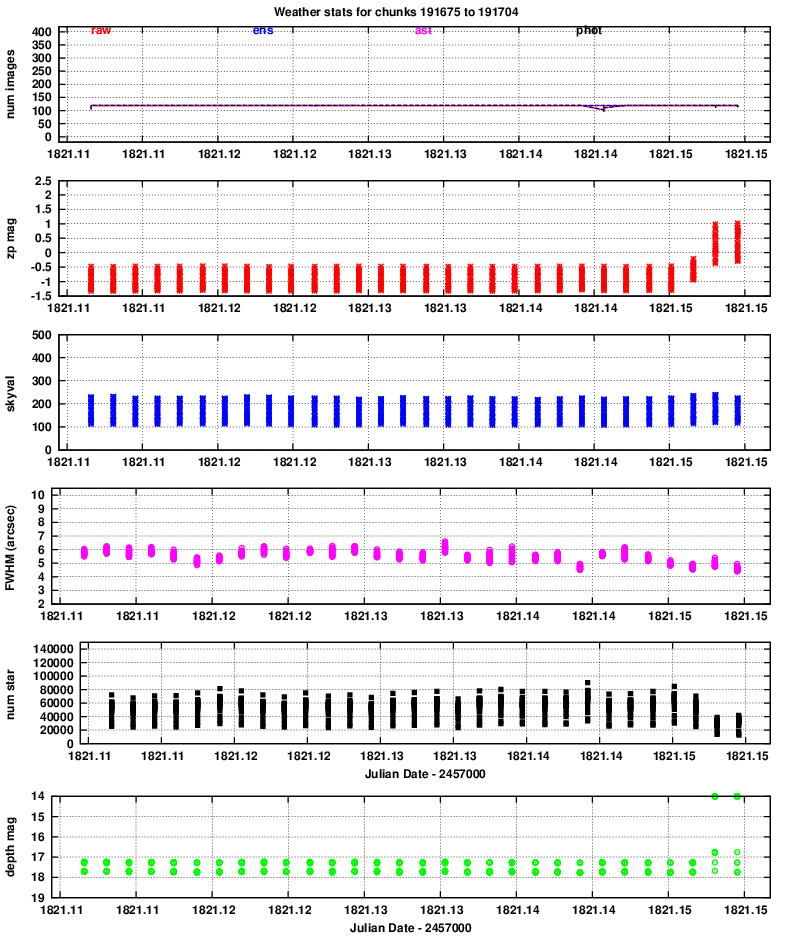
Quadrant 3:
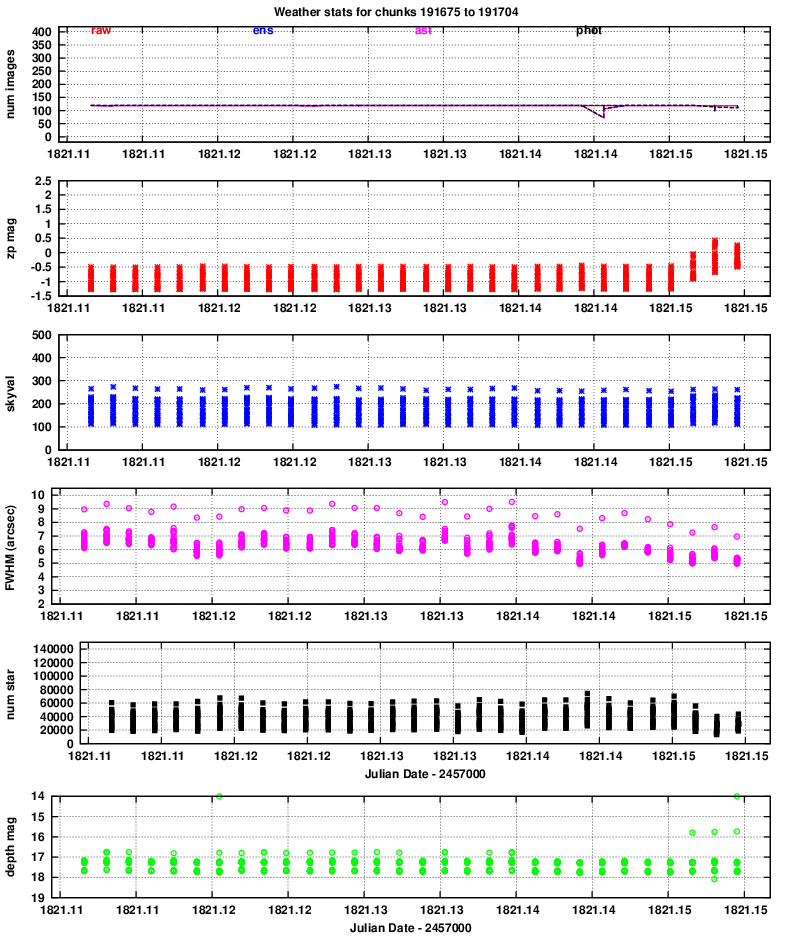
Quadrant 4:
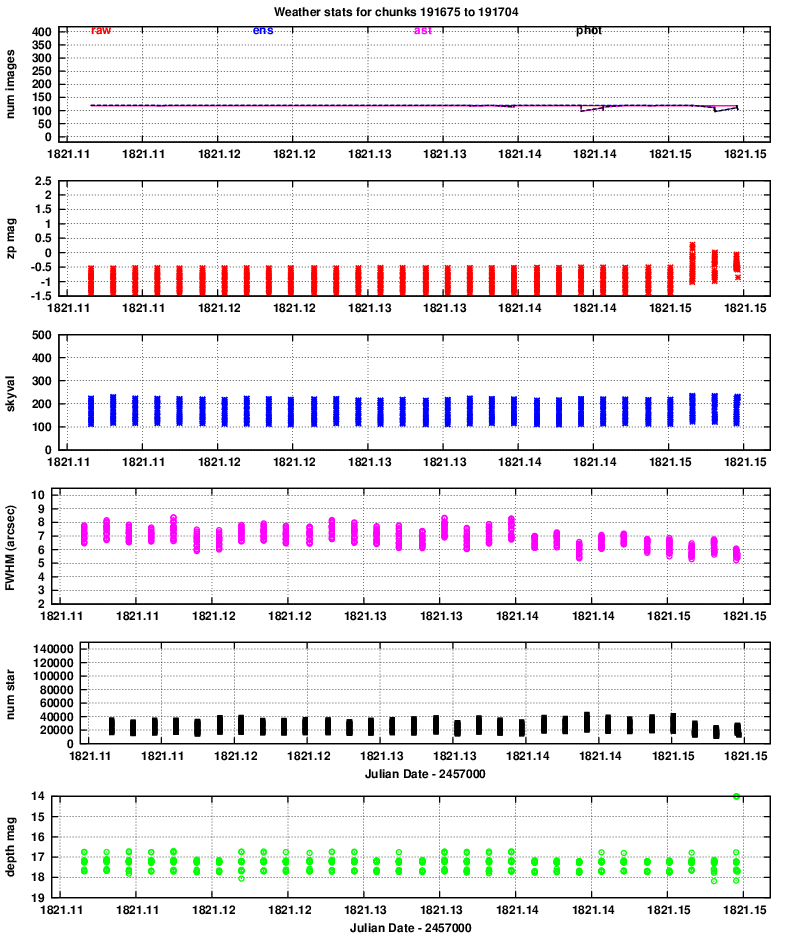
zp = (instrumental_mag) - (calibrated_mag)
Large positive values indicate extinction due to the atmosphere or clouds.
It seems that clouds appeared near the end of the run.
It is clear that the FWHM for quadrants 3 and especially 4 is (as usual) considerably larger than that of quadrants 1 and 2. Moreover, the FWHM is larger than usual overall -- I guess the atmosphere was turbulent this evening.
The images show that the "depth" is between mag 17 and 18 for the most part.
After all the data had been calibrated, I ran the "transient_a.pl" script, which applies the rules described in the Tomo-e transient search paper to look for sources with only a brief existence. The code also computes a "control time" for the dataset.
The software found 84, 109, 67, and 75 candidates in quadrants 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. I created a web page showing the properties of these candidates in each quadrant:
The entry for each candidate includes some information about the chunk in which it appears, its position in (x,y) pixel coordinates and (RA, Dec) coordinates, and its magnitude. The "variability score" describes the ratio of the standard deviation of its magnitudes away from the mean to the standard deviation from the mean of stars of similar brightness; so, a high score means the object is varying from frame to frame more than most objects of similar brightness.
The entries for quadrants 2, 3, and 4, contain columns listing the magnitudes of any objects at this position (to within 5 arcsec) in the USNO B1.0 (avergage of R-band magnitudes) and in the 2MASS catalog (K-band magnitude). A value of "99.0" indicates that no source appears in the catalog as this position. You can see that the overwhelming majority of candidates do correspond to objects which were detected in one or both of these catalogs -- meaning that they are not true transients.
After these columns of text, the documents contain thumbnails of the images around the candidate. The thumbnails are oriented with North up, East left, and are 110 pixels (= 130 arcsec) on a side.
Interesting candidates are:
The table below shows the control times for each quadrant in this dataset:
quadrant control time (square degrees * sec)
V=13 V=14 V=15 V=16 V=17
-------------------------------------------------------------
1 17953 17953 17817 7105 0
2 18109 18109 17425 8255 28
3 17247 17247 17028 1294 28
4 18001 18001 17584 978 0
total 71310 71310 69854 17632 56
-------------------------------------------------------------
These control times are comparable to to for each of the nights listed in the transient paper; It might be reasonable not to include this dataset in analysis, due to the poor weather.