On the night of Aug 11/12, 2025, under good conditions, I acquired images of the recurrent nova T CrB. This star undergoes outbursts at long intervals of 80 years or so. Its next outburst is predicted to occur soon (but then again, it was also predicted to occur during 2024), and so I've joined the crowd who are monitoring it.
Tonight's measurements are pretty good. A larger fraction of them are being made at high airmass, of course, and that fraction grows each night.
This recurrent nova brightens by about 8 magnitudes (!), from V = 10 to about V = 2, around every 80 years. Will we see another outburst THIS summer?
These observations involved:
Notes from the night:
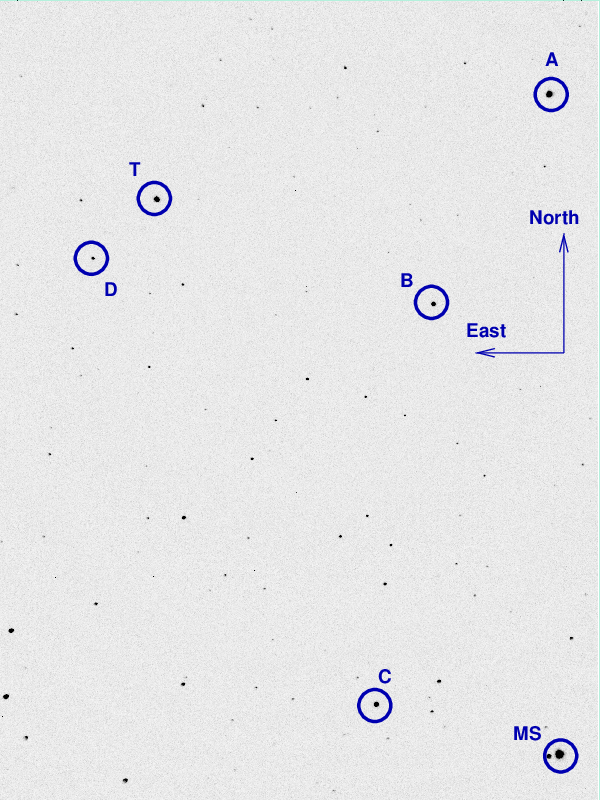
The picture below shows a cropped image of the field of T CrB from Jun 14/15, 2024. The field of view is about 20 arcminutes across.

I've marked the location of several comparison stars, with magnitudes and names taken from the AAVSO's table X40237AAS. Note that the magnitudes listed for stars "A" and "B" have changed from the ones I listed in last year's notes.
star name B V
------------------------------------------------------
A 000-BJS-901 11.096 10.554
B 000-BBW-805 11.779 11.166
C 000-BPC-198 13.049 12.336
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
When the target is centered, the finder TV shows this field:

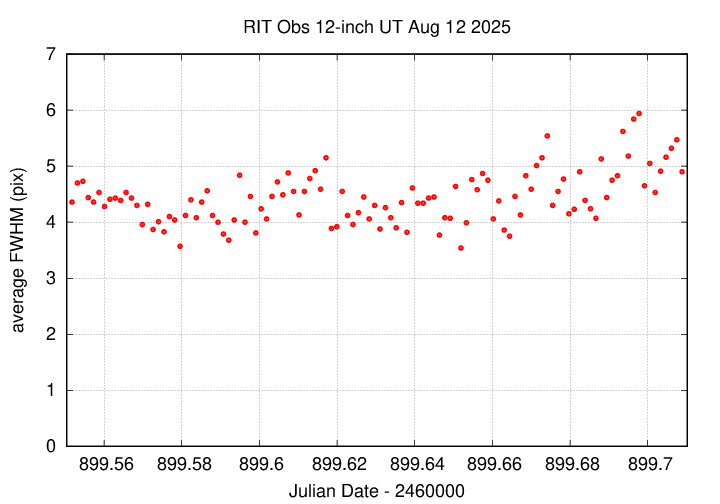
Here's the sky background over the course of the run. Pretty smooth, meaning no clouds.
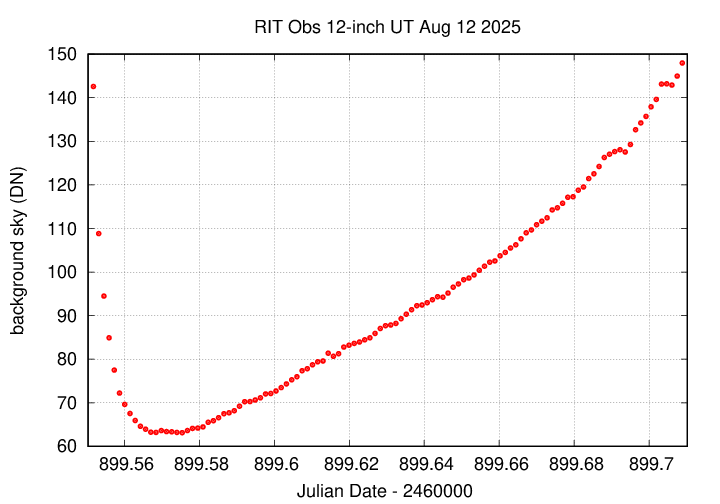
The FWHM rises just a bit at the end, due to airmass (I guess).
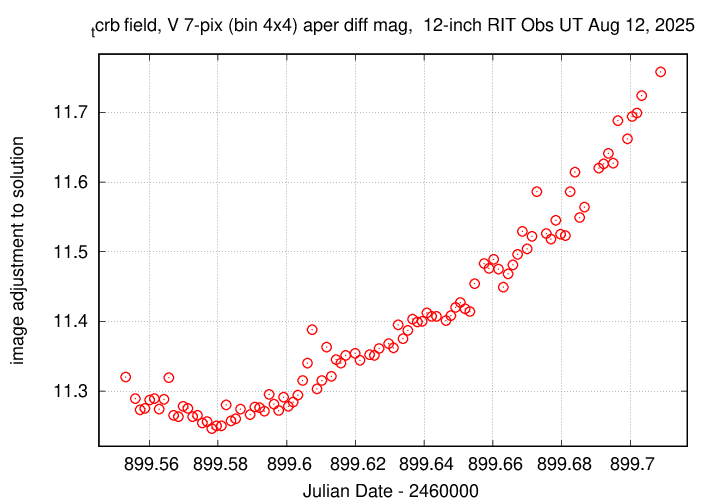
The graph below shows changes in the photometric zeropoint of an ensemble solution of the instrumental magnitudes over the course of the run. Not many outliers due to trailing, so the combination of custom tracking rate and 3-second guide exposures is working well.
Using aperture photometry with a radius of 7 pixels in V filter (binned 4x4, each pixel is 1.036 arcsec, so a radius of 7.3 arcsec), and 7 pixels in B filter (binned 4x4, each pixel is 1.036 arcsec, so a radius of 7.3 arcsec), I measured the instrumental magnitudes of a number of reference stars and the target. Following the procedures outlined by Kent Honeycutt's article on inhomogeneous ensemble photometry, I used all stars available in each image to define a reference frame, and measured each star against this frame.
Sigma-vs-mag plots show that the floor in V-band was about 0.008 mag in V, which is not bad; it was 0.010 in B -- not so great.
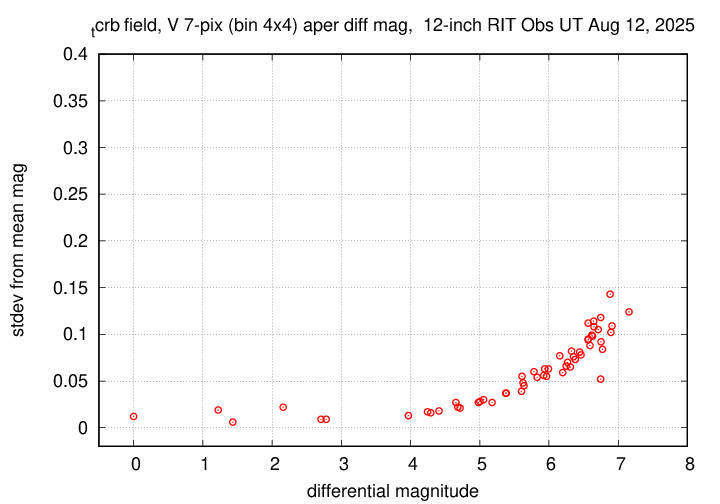
The measurements show that the target is still in quiescent phase.
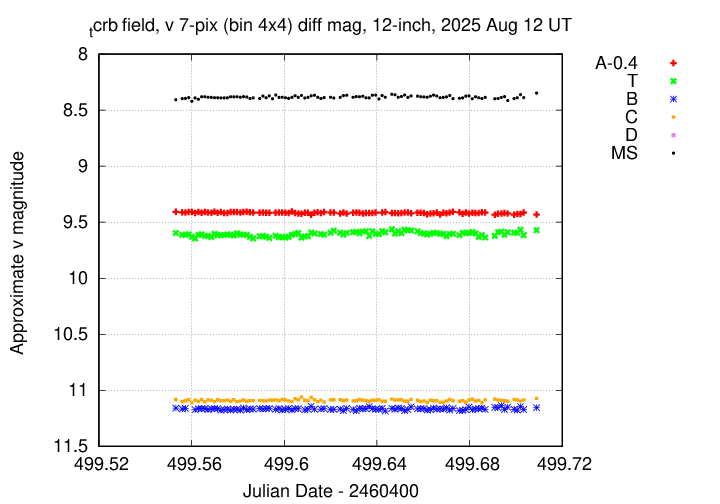
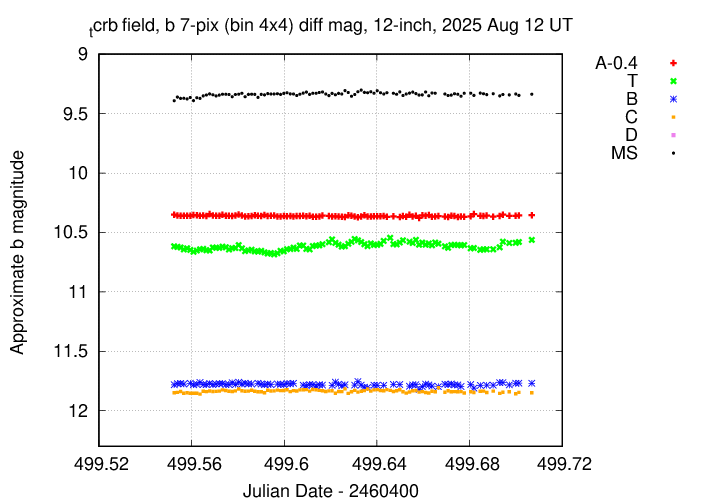
I've submitted these measurements to the AAVSO.