 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Review of Classical Mechanics
- Newton's Laws:
- Objects at rest remain at rest, in the absence of external
forces;
objects in motion remain in motion with constant
velocity, in the absence of external forces.
- F = ma
- For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
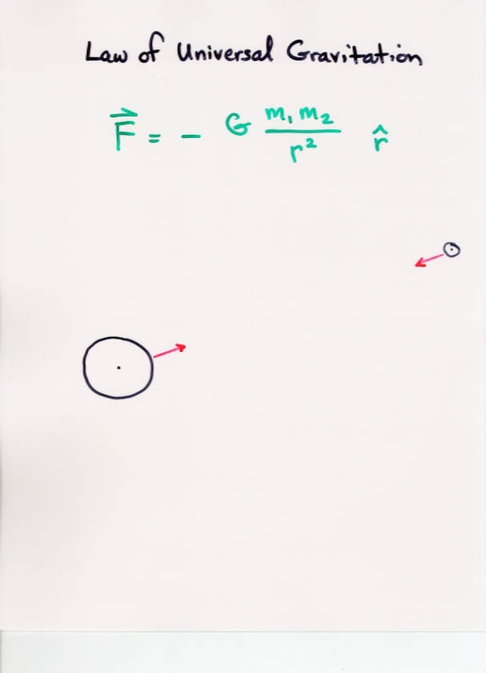
- Law of Universal Gravitation
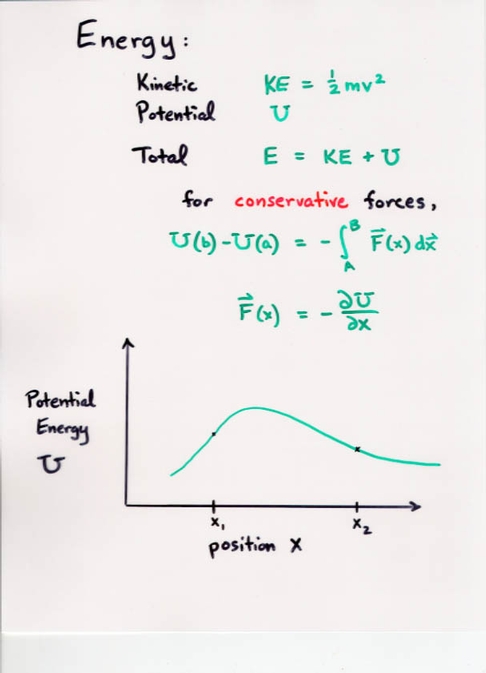
- Energy:
- Kinetic energy
- Potential energy
- Each conservative force
has an associated potential energy
- Conserved quantities:
- Energy
- Linear Momentum
- Angular Momentum
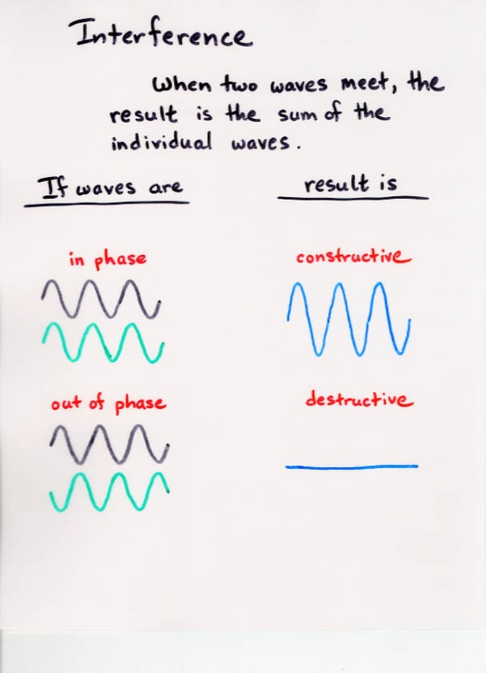
- Stationary waves can be described by
- amplitude
- wavelength or wave number
- phase
- Travelling waves can be described by
- amplitude
- wavelength or wave number
- angular frequency or frequency
- phase
- wave speed
- Observers moving relative to each other see
events happen in slightly different ways;
their descriptions are connected by
the Galilean transformations, e.g.
x' = x - v*t
- Time flows uniformly everywhere.
- All objects have a position and velocity.
-
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1
-
 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2
-
 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3
-
 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4
-
 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5
-
 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6
-
 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7
-
 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8
-
 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1  Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2  Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3  Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4  Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5  Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6  Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7  Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8  Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9  Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1  Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2  Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3  Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4  Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5  Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6  Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7  Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8  Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9  Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.