 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Gauss' Law
This lecture is based on HRW, Sections 24.4-24.9
- Electric charges are free to move around in and on a conductor,
which leads to these consequences:
- The charge density on the surface of a conductor
is uniform
- The electric field just above the surface of a conductor
is uniform, and points perpendicular to the surface
- The electric field INSIDE a conductor is zero
- Gauss' Law relates the charge within a closed surface to the
electric flux through that surface
- Problems with strong symmetry are good candidates for solution via
Gauss' Law:
- large flat planes covered uniformly with charge
- spheres or cylinders covered uniformly with charge
- lines of uniform charge density
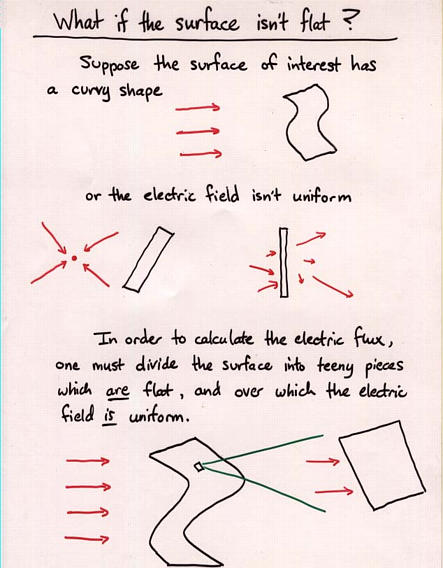 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1
 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2
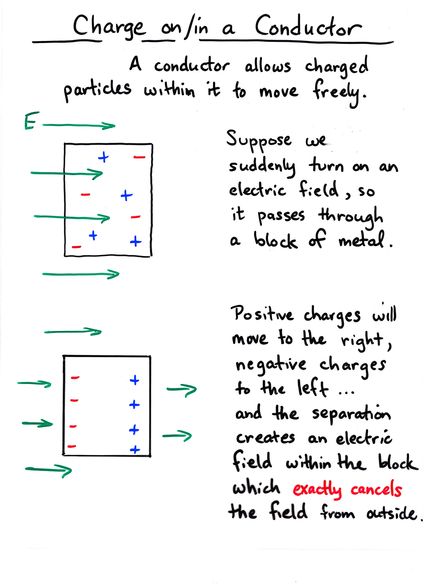 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3
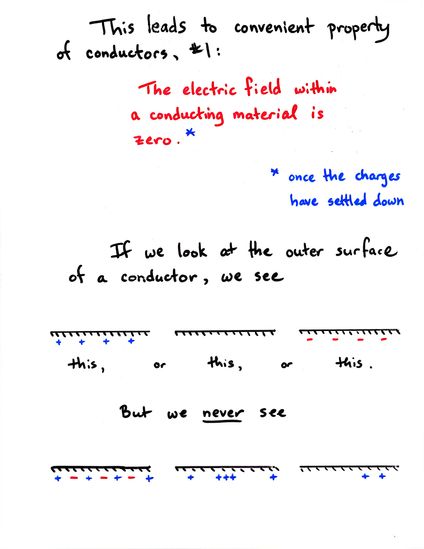 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4
 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5
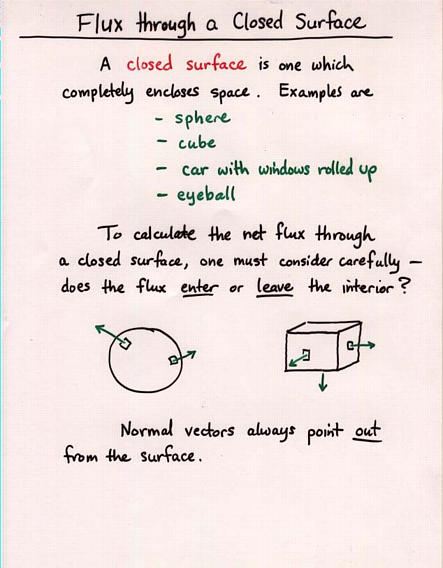 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6
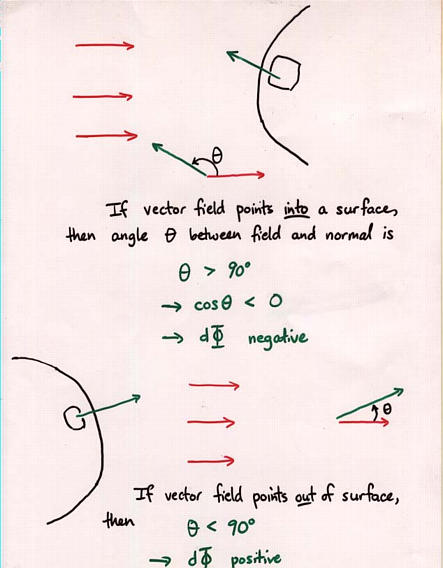 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7
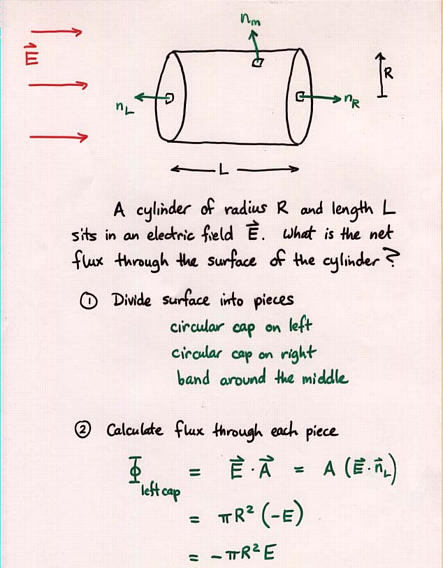 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8
 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9
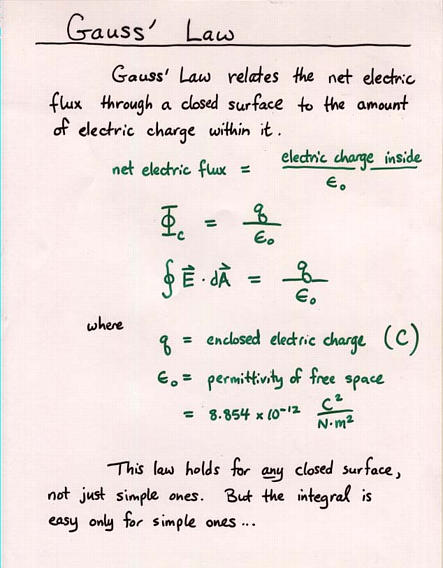 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10
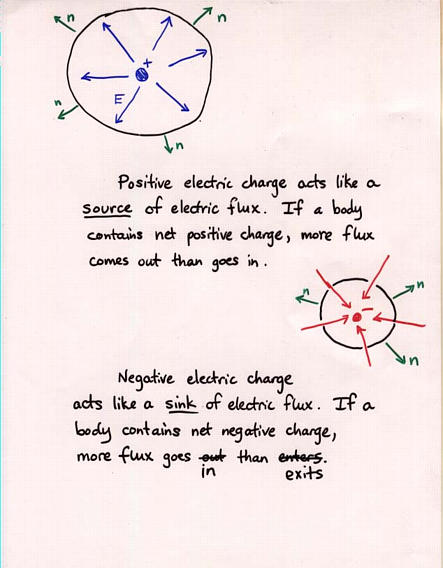 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11
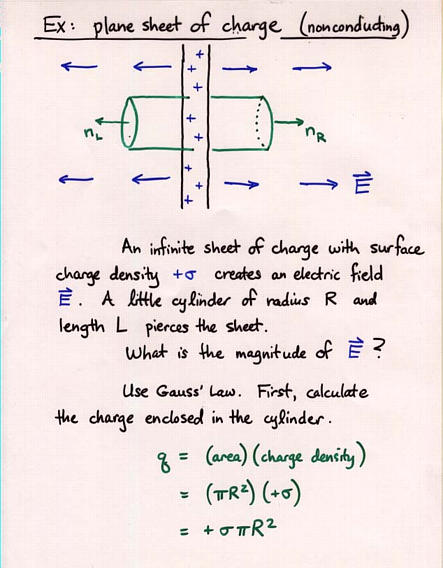 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12
 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13
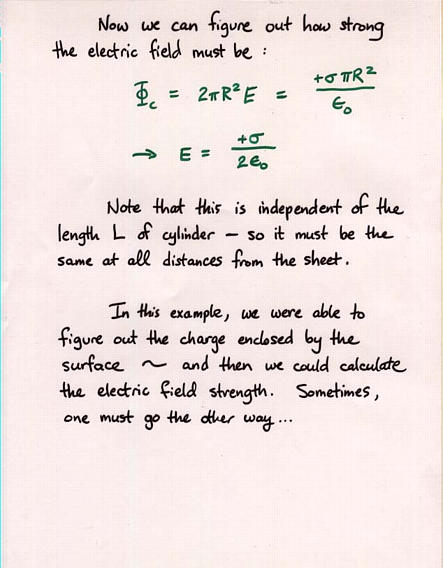 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14
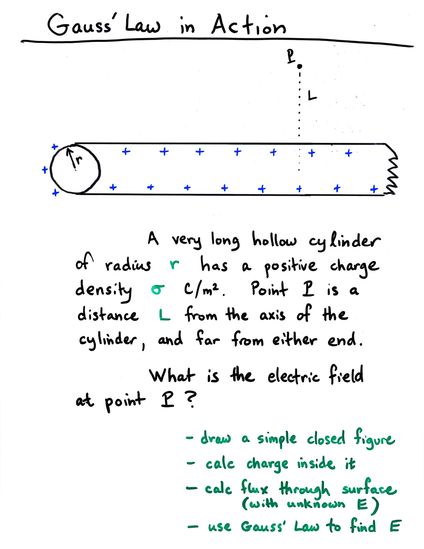 Viewgraph 15
Viewgraph 15
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13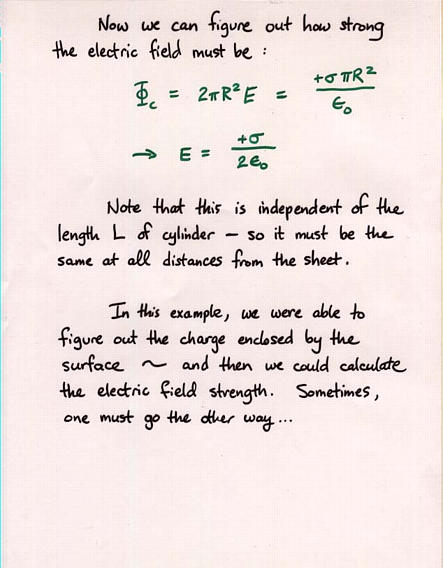 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14 Viewgraph 15
Viewgraph 15 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.