 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11
 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12
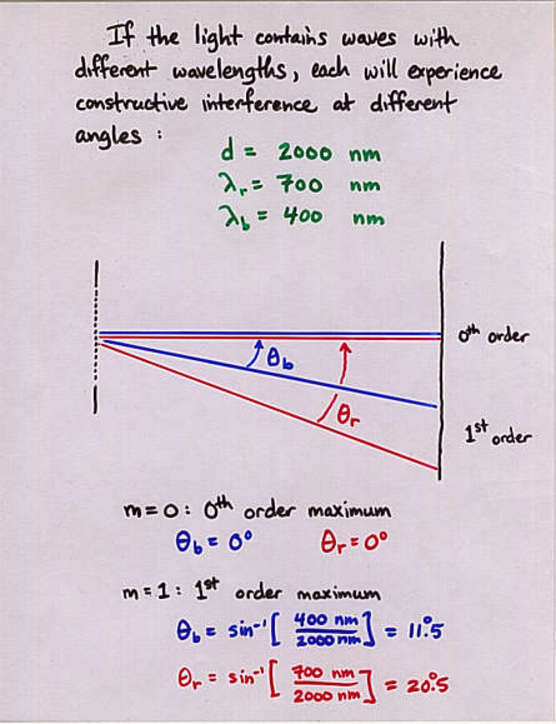 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13
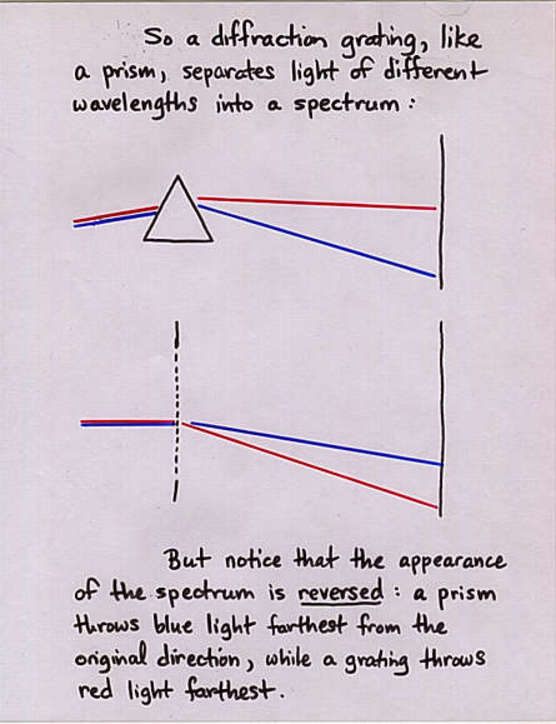 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14
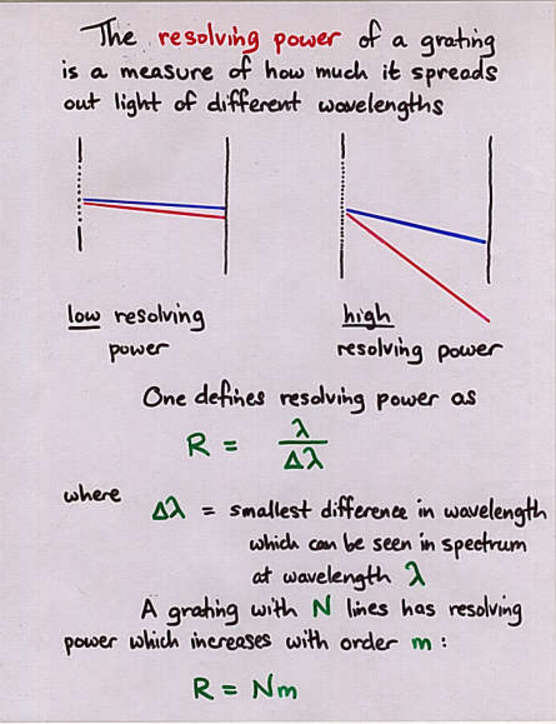 Viewgraph 15
Viewgraph 15
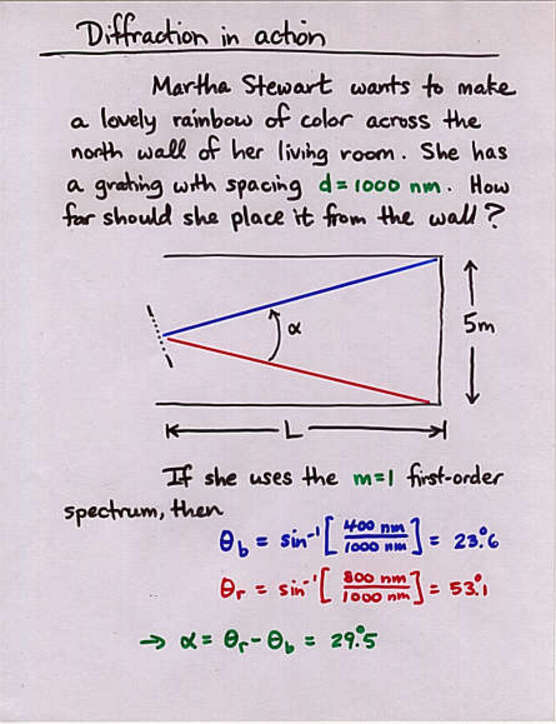 Viewgraph 16
Viewgraph 16
 Viewgraph 17
Viewgraph 17
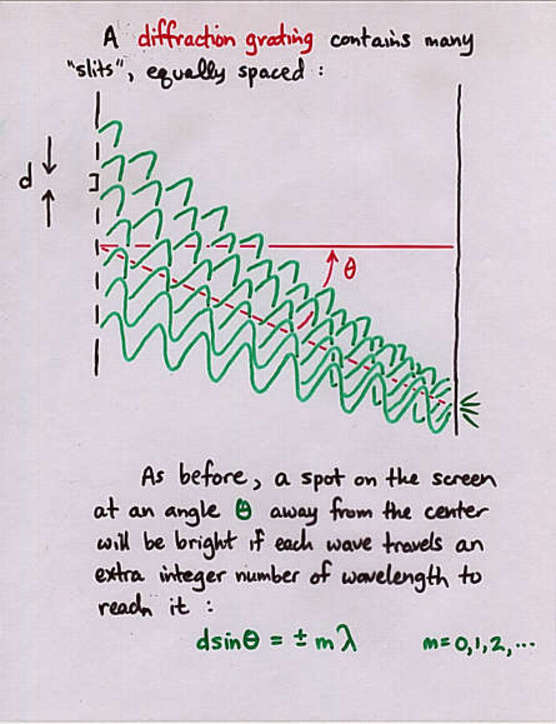
d sin(theta) = m lambda m = 1, 2, 3, ...
where "d" is the spacing of the slits
 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11
 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12
 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13
 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14
 Viewgraph 15
Viewgraph 15
 Viewgraph 16
Viewgraph 16
 Viewgraph 17
Viewgraph 17