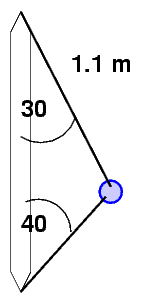
For starters, ignore the force of gravity on the ball ....
- What is the length of the bottom string?
- What is the acceleration of the ball?
- What is the net force applied to the ball by the strings?
- What is the tension in the top string?
- What is the tension in the bottom string?
What happens if you include the force of gravity, too?
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.