 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1
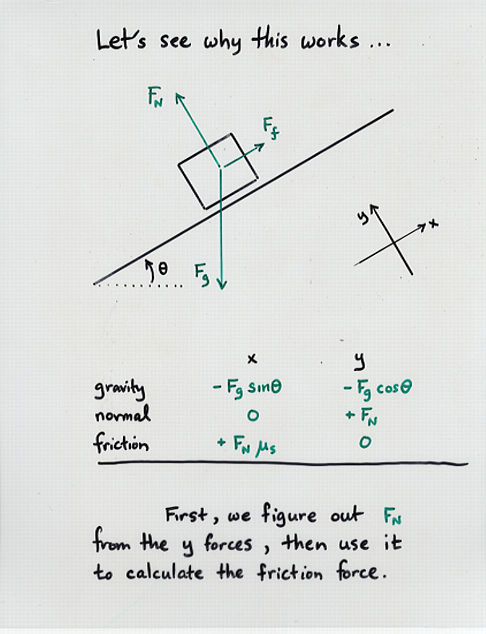 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2
 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3
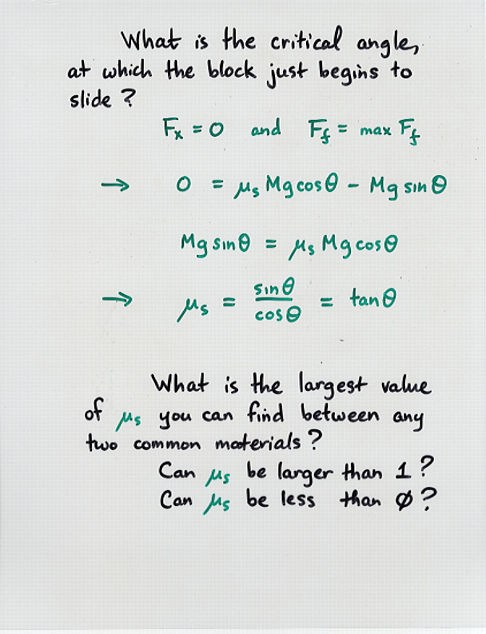 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4
 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5
 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6
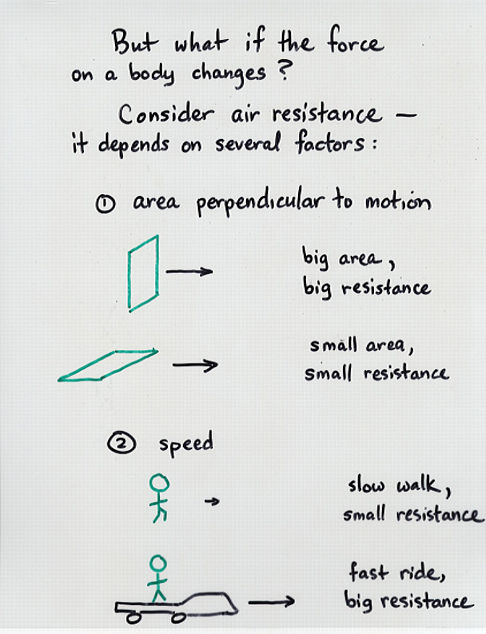 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7
 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8
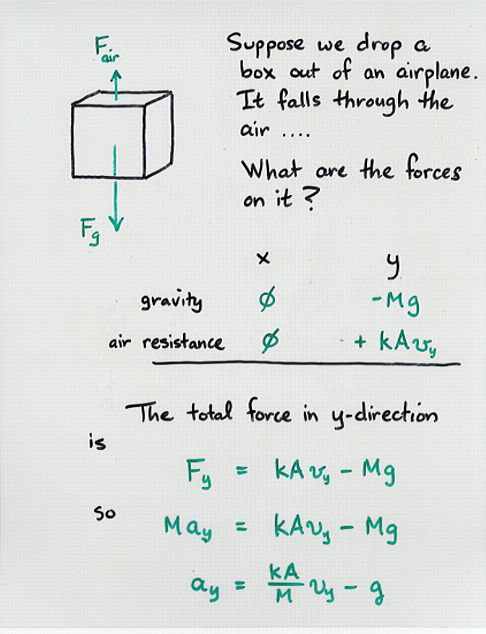 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9
 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10
Now, faced with a differential equation, we can try to solve it analytically (pencil and paper), or numerically (with a computer). Let's try both methods.
Analytical solutions
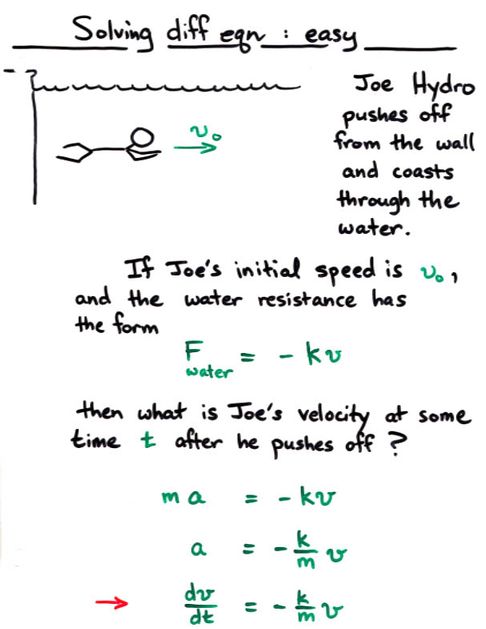 Viewgraph 10a
Viewgraph 10a
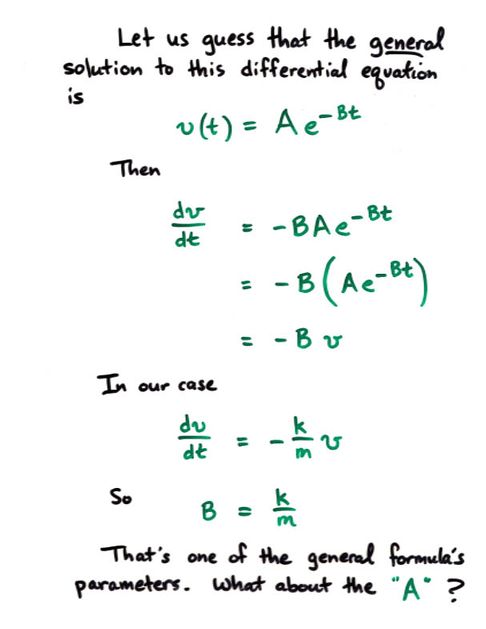 Viewgraph 10b
Viewgraph 10b
 Viewgraph 10c
Viewgraph 10c
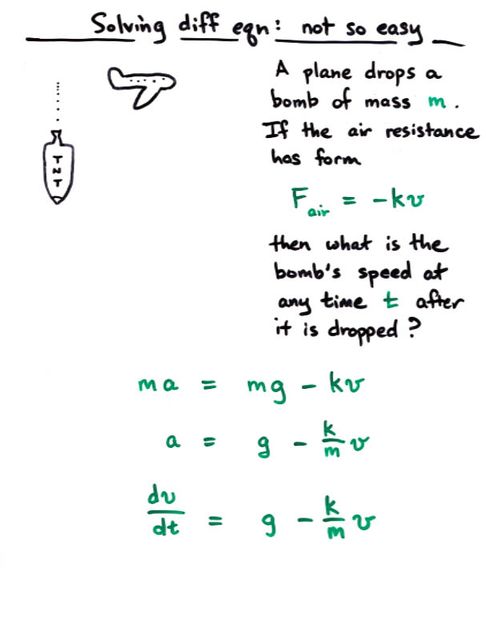 Viewgraph 10d
Viewgraph 10d
 Viewgraph 10e
Viewgraph 10e
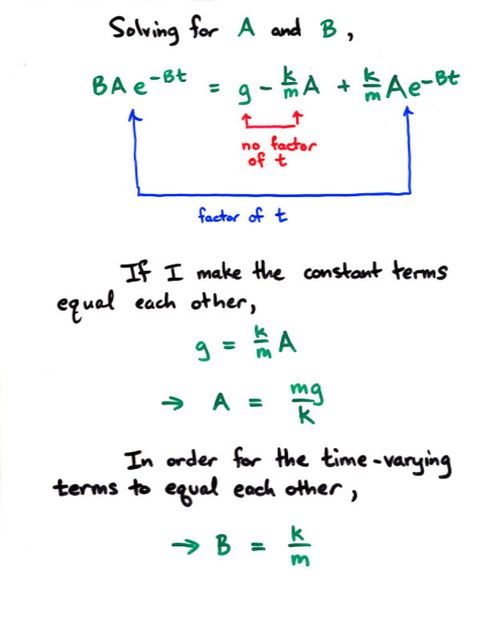 Viewgraph 10f
Viewgraph 10f
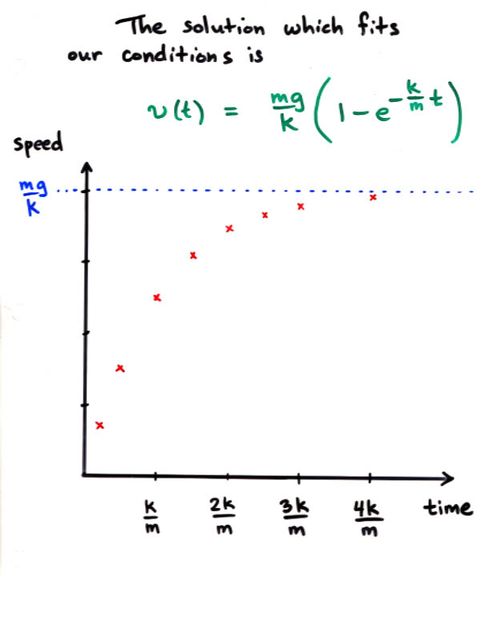 Viewgraph 10g
Viewgraph 10g
Numerical solutions
 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11
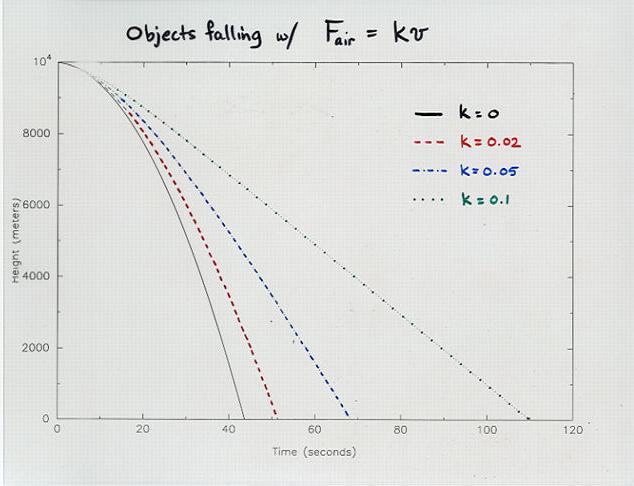 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12
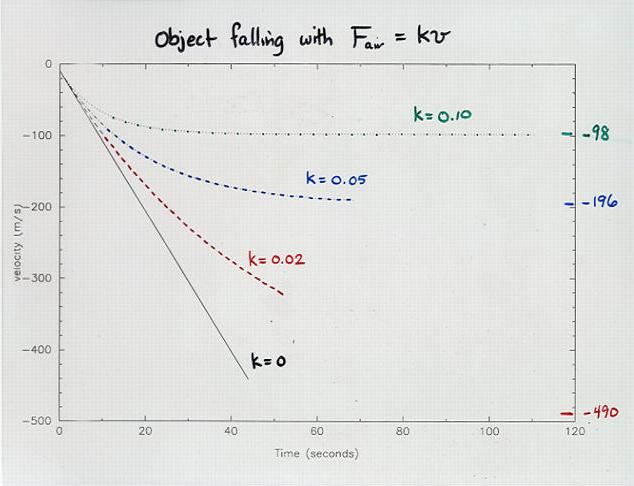 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13
Terminal Velocity
 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14
 Viewgraph 15
Viewgraph 15
 Viewgraph 16
Viewgraph 16
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.