 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1
 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2
 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3
 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4
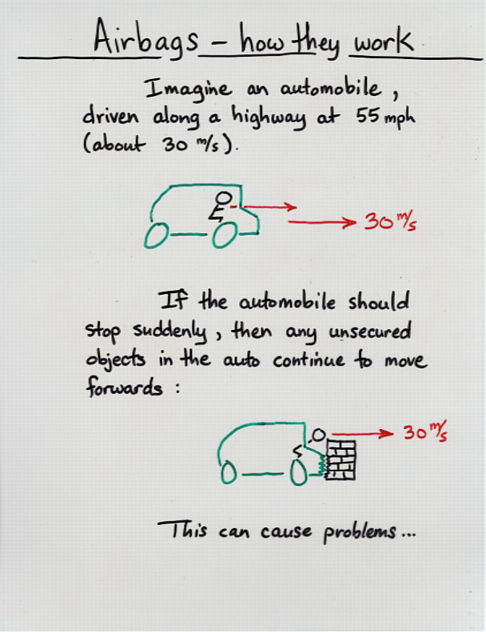 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5
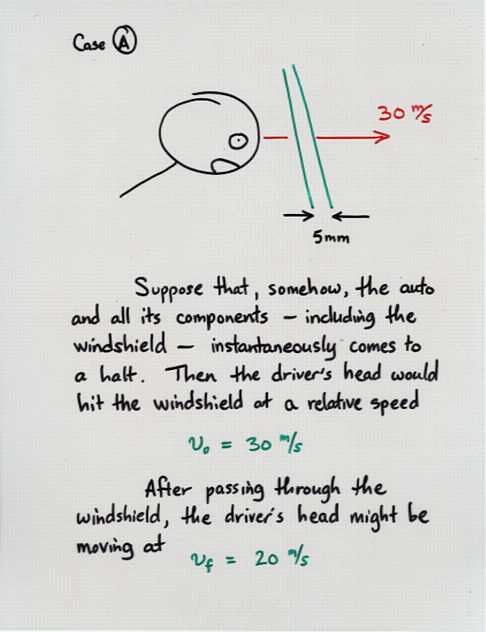 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6
 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7
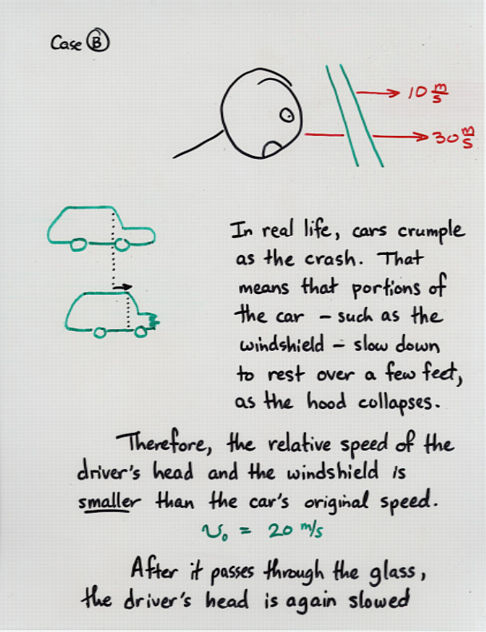 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8
 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9
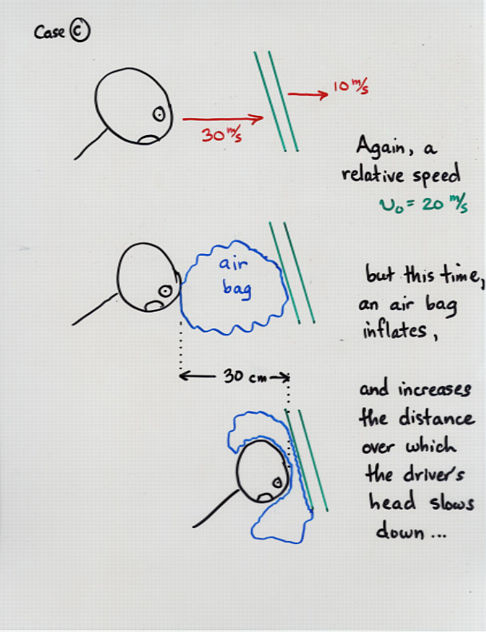 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10
 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11
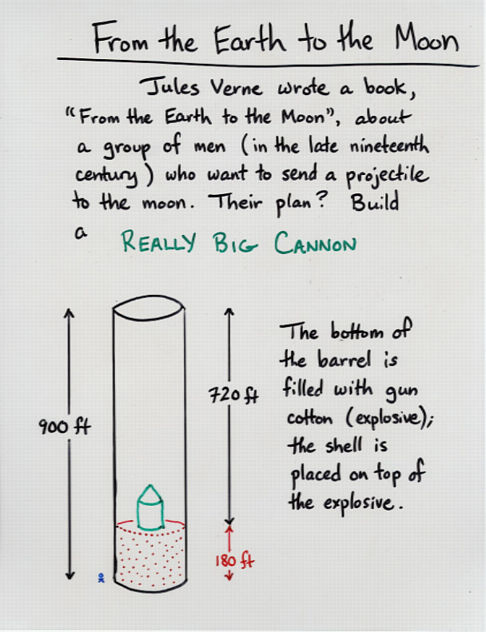 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12
 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13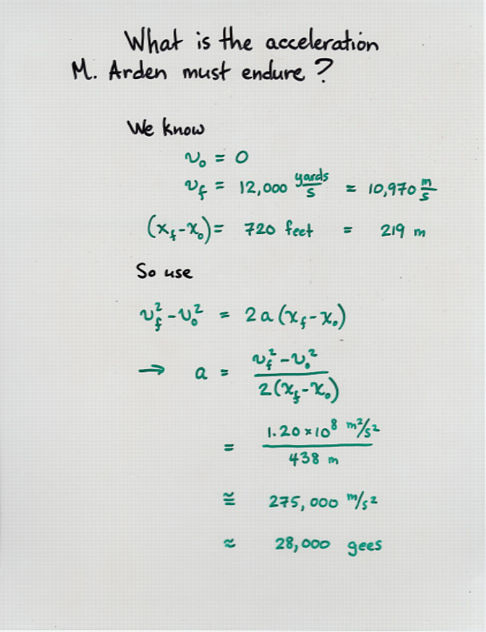 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14
 Viewgraph 15
Viewgraph 15
 Viewgraph 16
Viewgraph 16
 Viewgraph 17
Viewgraph 17
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
g = 9.8 m/s^2
which is the magnitude of acceleration due to earth's gravity.
Thus, for most objects in flight,
ax = 0 horizontally
ay = -g vertically
Viewgraphs
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1
 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2
 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3
 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4
 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5
 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6
 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7
 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8
 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9
 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10
 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11
 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12
 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13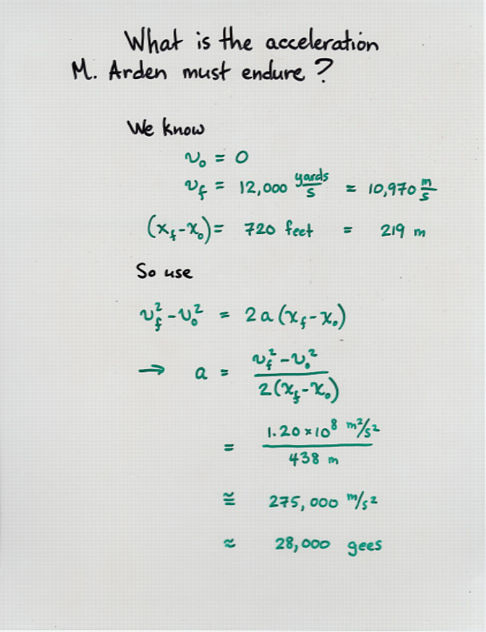 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14
 Viewgraph 15
Viewgraph 15
 Viewgraph 16
Viewgraph 16
 Viewgraph 17
Viewgraph 17
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.