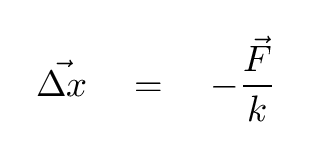
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Starting next class, we will begin to investigate oscillatory motion. One of the simplest oscillating systems is a mass attached to a spring. If the mass and spring are initial at rest, in equilibrium, and then you displace the mass by a distance x = 5 cm, you can figure out the size of the restoring force of the spring:
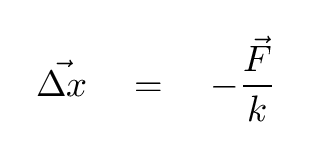
But what if someone displaces the mass and tells you, not the absolute size of the displacement, but only the fractional (or percentage) size of the displacement -- is there anything you can deduce from that?
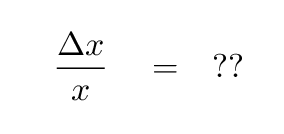
YES. The study of relative changes in size or position due to applied forces and pressures involves a quantity called ELASTICITY. You will find out later today that there is a very close connection between
RELATIVE displacements ABSOLUTE displacements
----------------------- -------------------------
Young's modulus E force constant k
strain modulus S
bulk modulus B
The "modulus" properties of materials are very, very important for engineers, since they describe what will happen to an object -- such as a beam or pillar or strut -- when it is placed under some stress.
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.