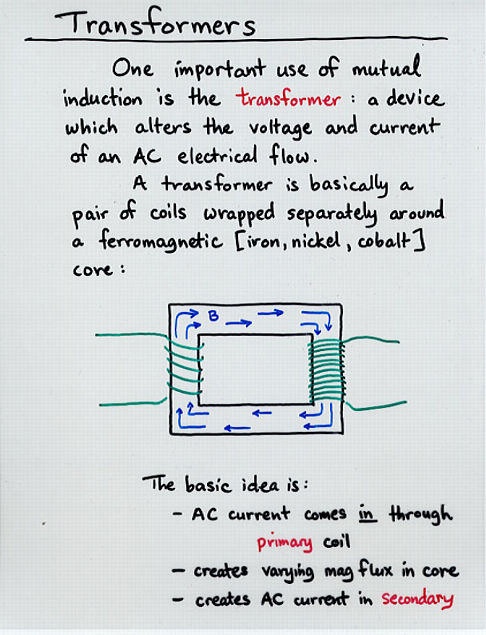
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Vs Ns Ip
---- = ---- = ----
Vp Np Is
Ns > Np step-up transformer
Ns < Np step-down transformer
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1
 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2
 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3
 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4
Let's look very briefly at the steps involved in bringing electricity from a generating station to your home. For the full story, read How Power Distribution Grids Work, in the references below.
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.