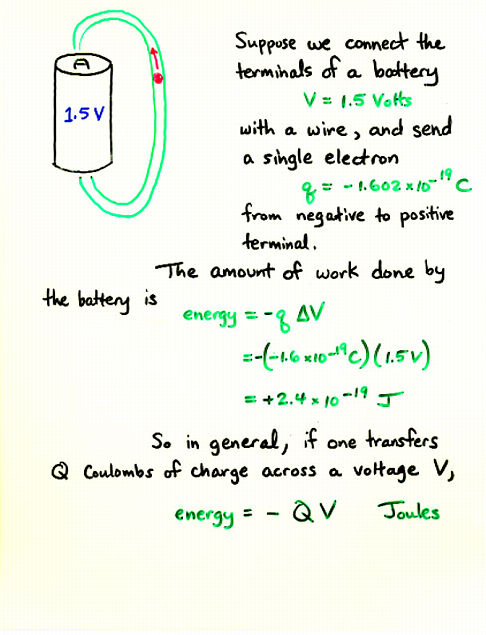
 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Power = (current)*(voltage) Watts
Energy = P*t Joules
1 kWh = (1 kilowatt) * (1 hour) = 3,600,000 Joules
V(rms) = V(peak) / sqrt(2) = 0.707 V(peak)
I(rms) = I(peak) / sqrt(2) = 0.707 I(peak)
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1
 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2
 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3
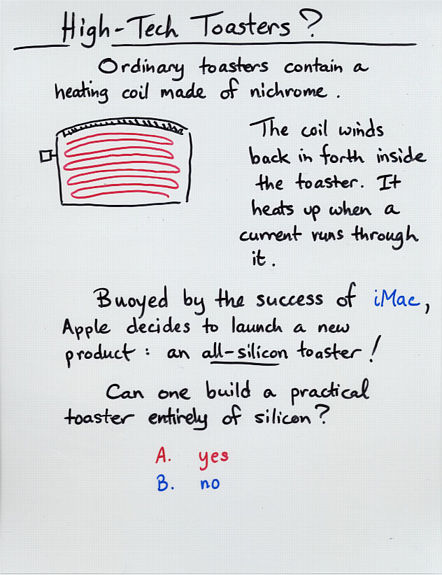 Viewgraph 3a
Viewgraph 3a
 Viewgraph 3b
Viewgraph 3b
 Viewgraph 3c
Viewgraph 3c
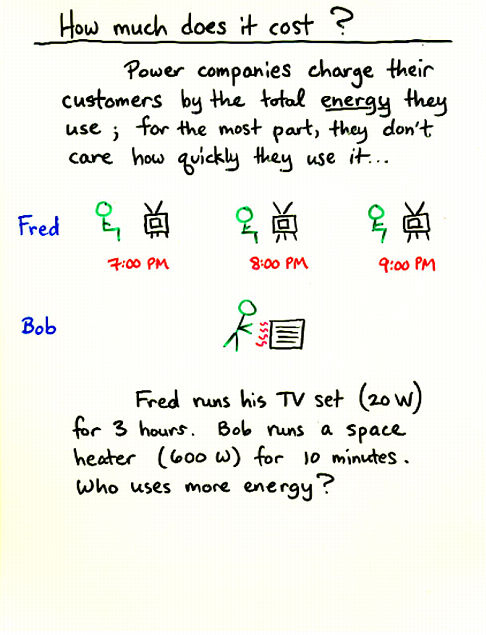 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4
 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5
 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6
 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7
 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8
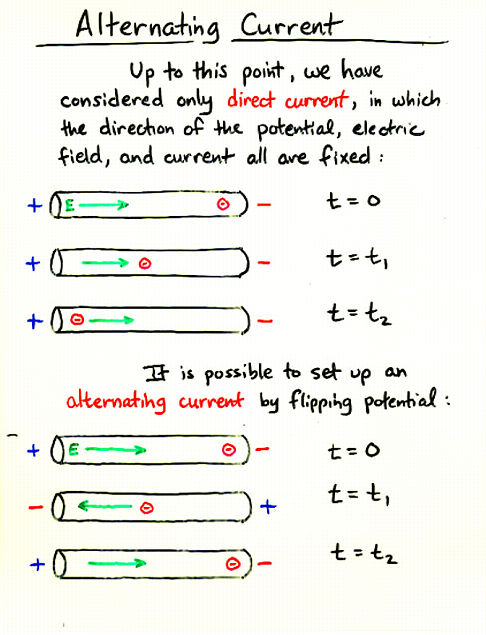 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9
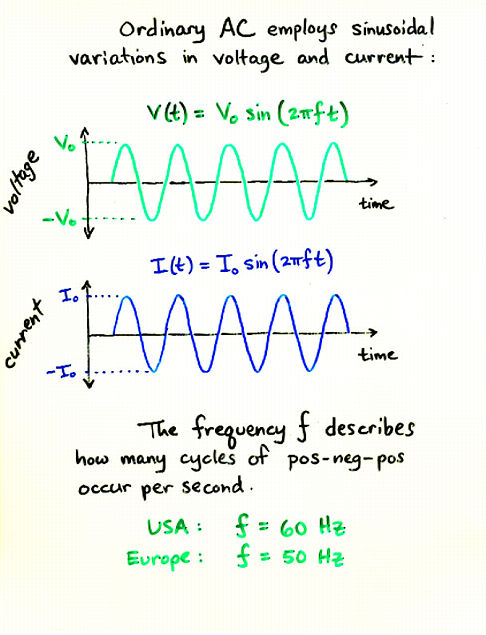 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10
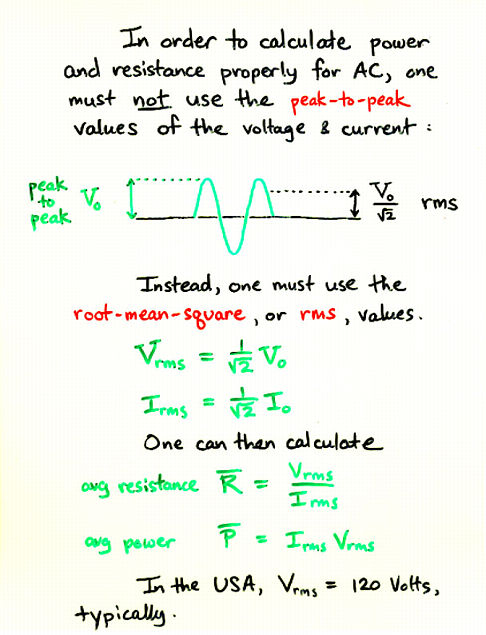 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.