 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Measuring current and Household Wiring
- Magnetic fields exert force on a current-carrying wire;
we can use these forces to measure the current.
- A galvanometer is a simple device to measure
current via deflection of a current-carrying wire in a
magnetic field.
- By splitting the current through an ammeter into several
pieces via shunt resistors, one can extend its range.
- Typical houses contain several circuits, all connected in parallel
to the external power supply. Each circuit is rated to carry at
most a certain current (typically 10 to 30 amps)
- Each circuit contains a circuit breaker, or a fuse,
to prevent larger currents from flowing
- Three-prong wires contain a special ground wire which
carries any stray current through an appliance away from
human touch.
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1
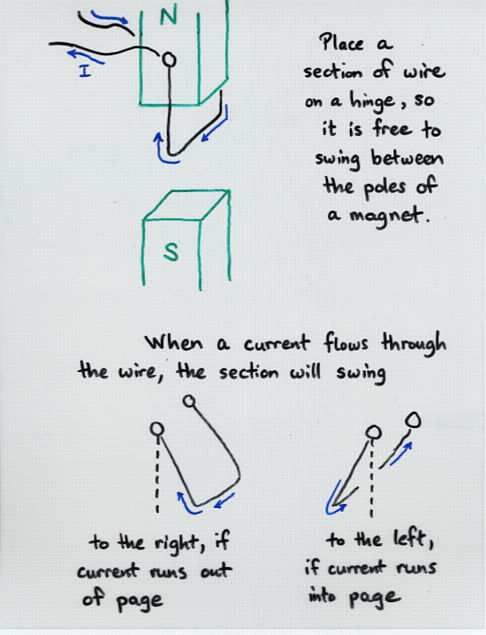 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2
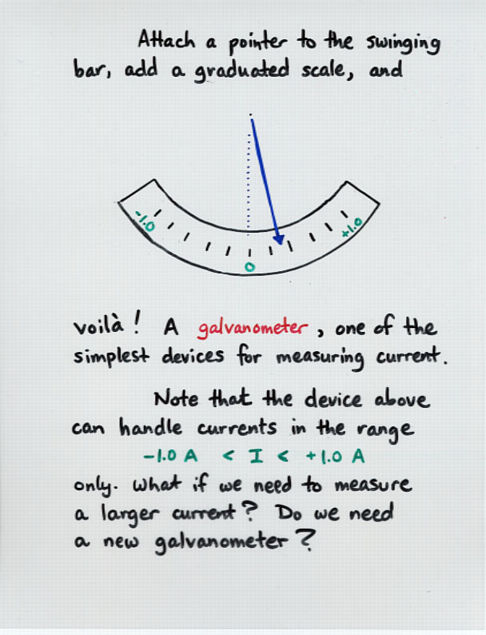 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3
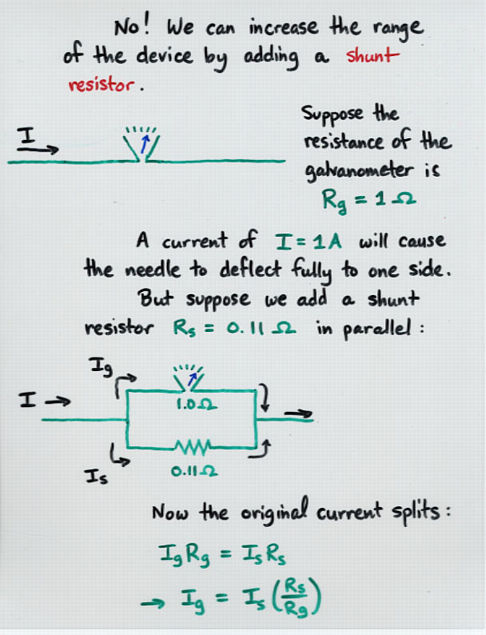 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4
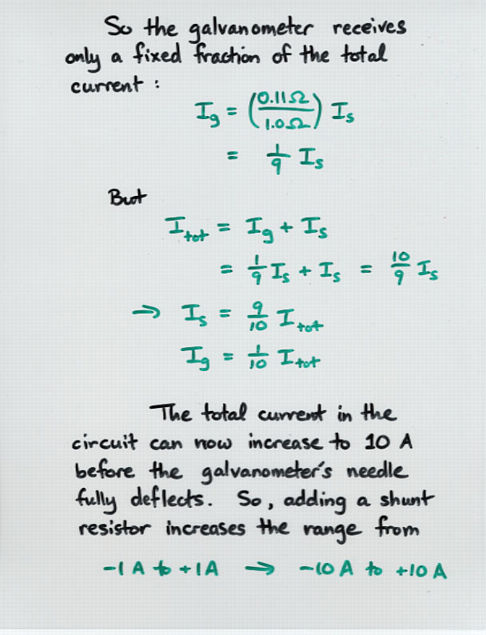 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5
 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6
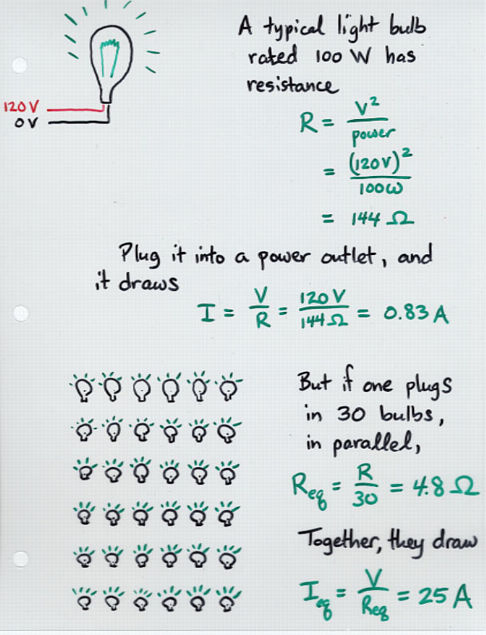 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7
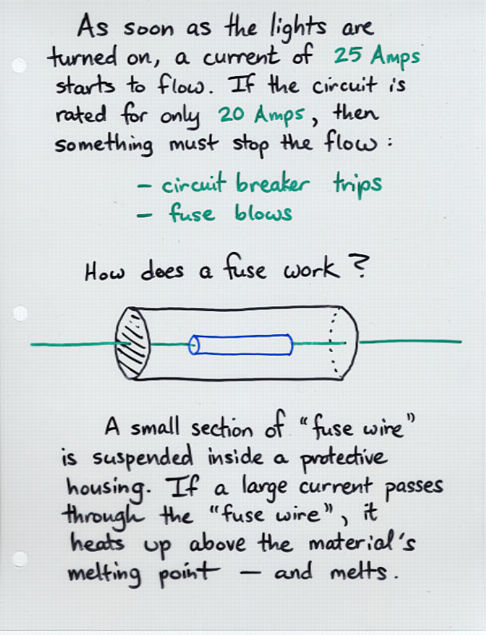 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8
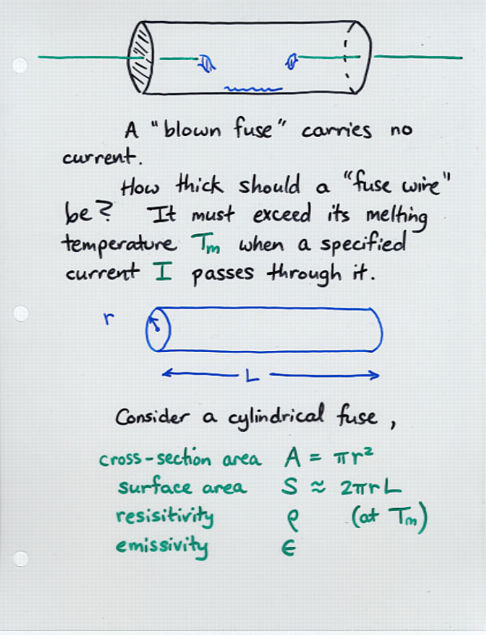 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9
 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10
 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11
 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12
 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13
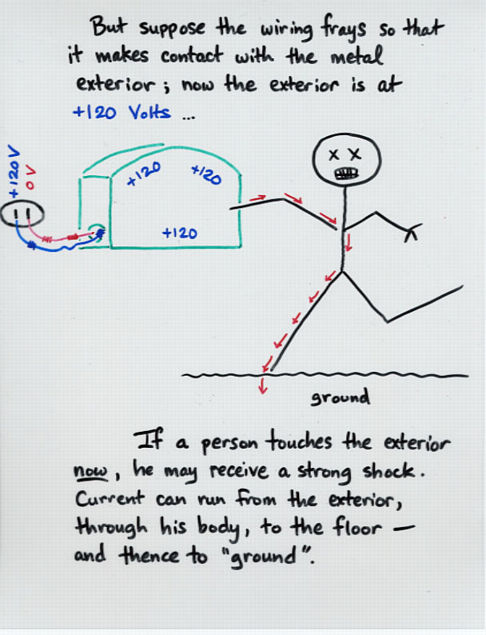 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14
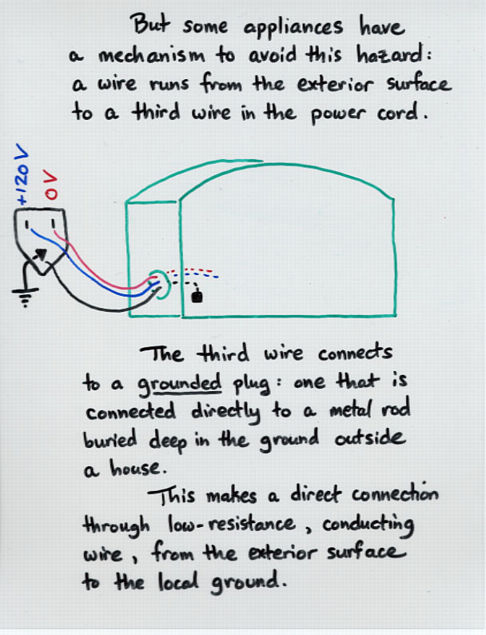 Viewgraph 15
Viewgraph 15
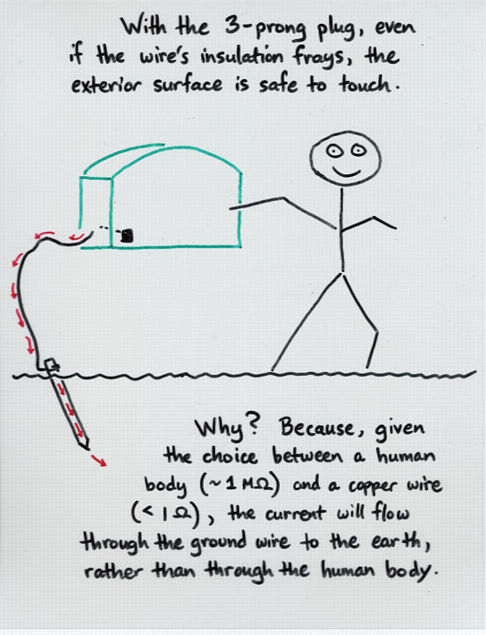 Viewgraph 16
Viewgraph 16
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14 Viewgraph 15
Viewgraph 15 Viewgraph 16
Viewgraph 16 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.