 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
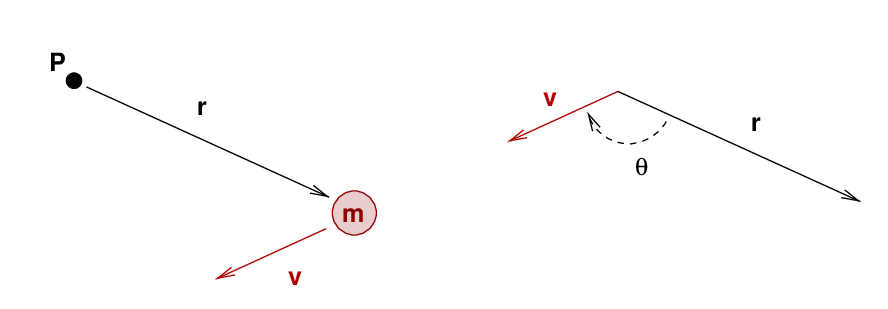
If a compact object is far from some axis and moving with some velocity, then we can compute its angular momentum around that axis using the cross product:

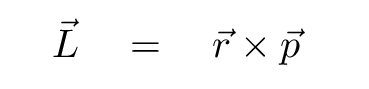
The DIRECTION of the angular momentum is given by the same right-hand-rule we use for the cross product.
Let's look at an astronomical example:
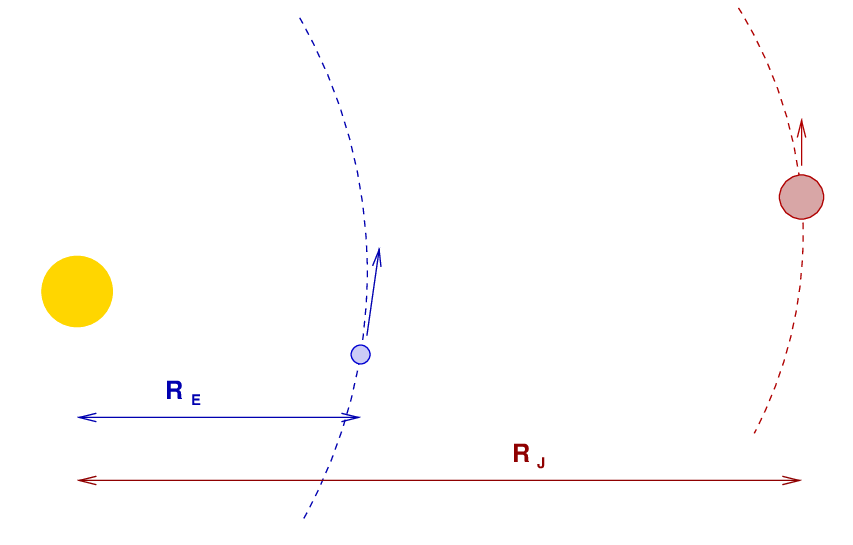
The Earth and Jupiter orbit the Sun. The Sun rotates around its own axis.
Body Mass Period Radius Orbital radius
(kg) (m) (m)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sun 1.99 x 1030 1 month 6.96 x 108 ---
Earth 5.98 x 1024 1 year ---- 1.50 x 1011
Jupiter 1.90 x 1027 11.85 year ---- 7.78 x 1011
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Can you determine the magnitude and direction of
Q: The Sun's spin angular momentum around its own axis?
Q: The Earth's orbital angular momentum around the Sun?
Q: Jupiter's orbital angular momentum around the Sun?
Q: Where is most of the angular momentum in the solar system?
 Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Copyright © Michael Richmond.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.