Physics 312 Lecture: "Angular Momentum"
Mar 19, 1998
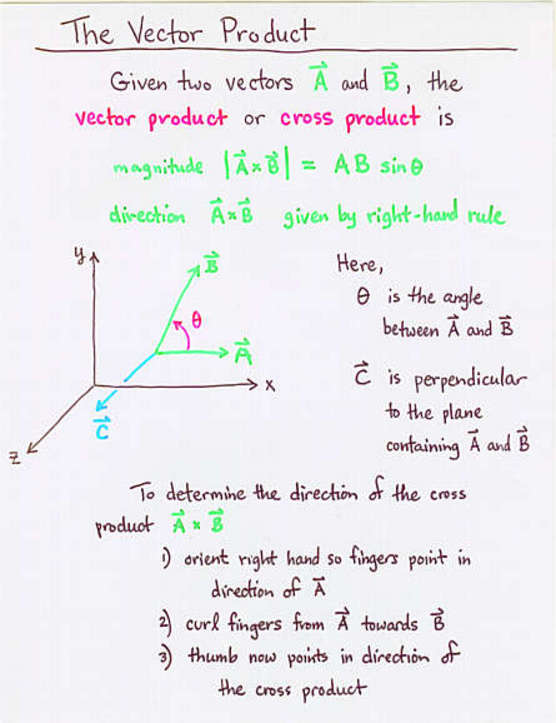
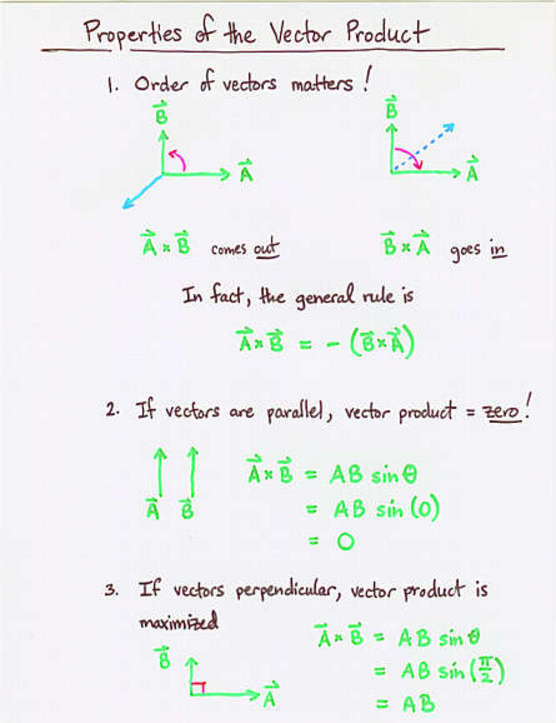
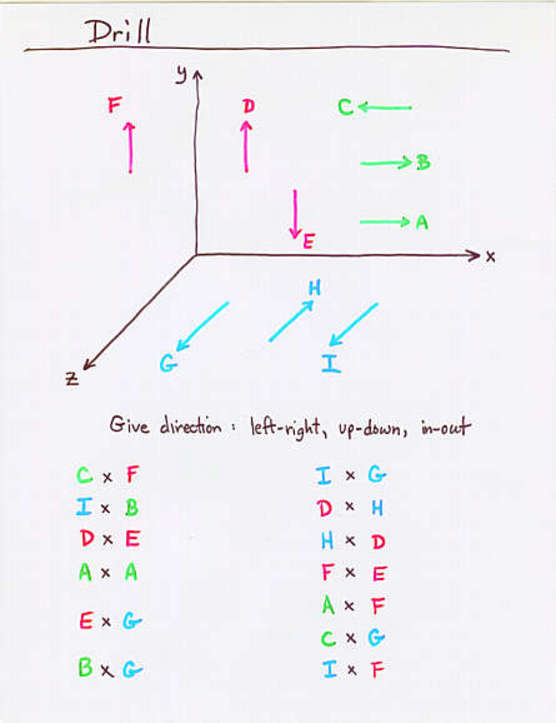
- The vector or cross product is another way to combine two
vectors; it creates a vector perpendicular to both
it the originals.
- The angular momentum of a body depends on the point chosen
as the origin.
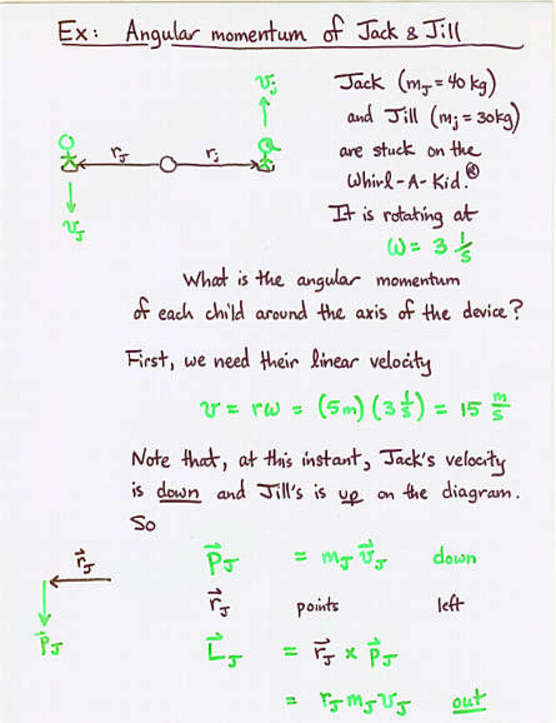
- The angular momentum of a body around a point is the cross
product of the radius from the point to the body
and the momentum of the body.
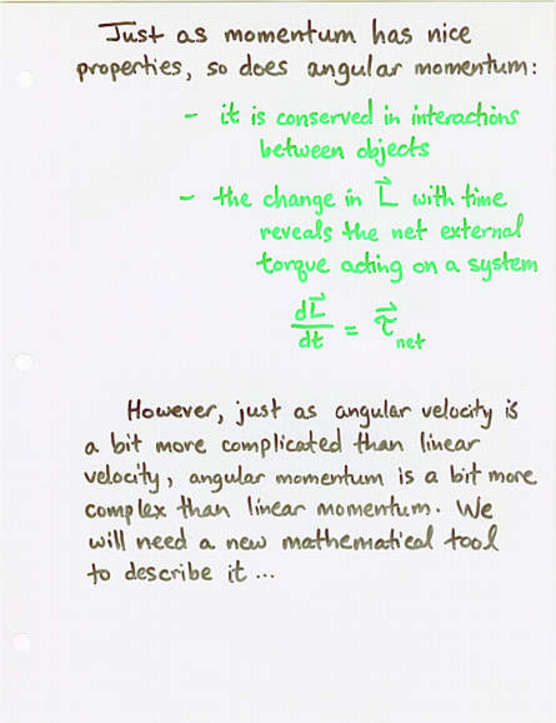
- Angular momentum is the rotational analog of linear momentum
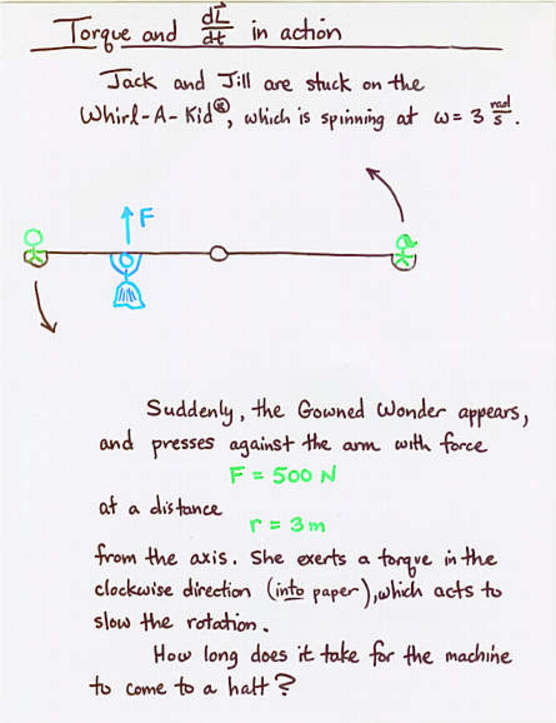
- Just as the time derivative of linear momentum is force,
the time derivative of angular momentum is torque.
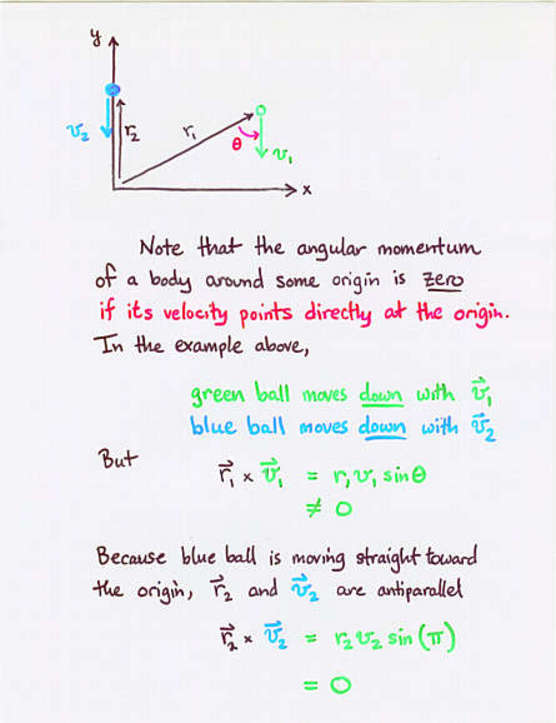
- The angular momentum around a point of a body which moves directly
towards that point is zero.
This lecture discusses material in Chapter 11 of Serway.
-
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1
-
 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2
-
 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3
-
 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4
-
 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5
-
 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6
-
 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7
-
 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8
-
 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9
-
 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10
-
 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11
-
 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12
-
 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13
-
 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14
 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14 Viewgraph 1
Viewgraph 1 Viewgraph 2
Viewgraph 2 Viewgraph 3
Viewgraph 3 Viewgraph 4
Viewgraph 4 Viewgraph 5
Viewgraph 5 Viewgraph 6
Viewgraph 6 Viewgraph 7
Viewgraph 7 Viewgraph 8
Viewgraph 8 Viewgraph 9
Viewgraph 9 Viewgraph 10
Viewgraph 10 Viewgraph 11
Viewgraph 11 Viewgraph 12
Viewgraph 12 Viewgraph 13
Viewgraph 13 Viewgraph 14
Viewgraph 14